使用(哈希)密码和 JWT Bearer 令牌的 OAuth2¶
既然我们已经有了所有的安全流程,就让我们来使用 JWT 令牌和安全哈希密码让应用程序真正地安全吧。
你可以在应用程序中真正地使用这些代码,在数据库中保存密码哈希值,等等。
我们将从上一章结束的位置开始,然后对示例进行扩充。
关于 JWT¶
JWT 表示 「JSON Web Tokens」。
它是一个将 JSON 对象编码为密集且没有空格的长字符串的标准。字符串看起来像这样:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
它没有被加密,因此任何人都可以从字符串内容中还原数据。
但它经过了签名。因此,当你收到一个由你发出的令牌时,可以校验令牌是否真的由你发出。
通过这种方式,你可以创建一个有效期为 1 周的令牌。然后当用户第二天使用令牌重新访问时,你知道该用户仍然处于登入状态。
一周后令牌将会过期,用户将不会通过认证,必须再次登录才能获得一个新令牌。而且如果用户(或第三方)试图修改令牌以篡改过期时间,你将因为签名不匹配而能够发觉。
如果你想上手体验 JWT 令牌并了解其工作方式,可访问 https://jwt.io。
安装 python-jose¶
我们需要安装 python-jose 以在 Python 中生成和校验 JWT 令牌:
$ pip install python-jose[cryptography]
---> 100%
Python-jose 需要一个额外的加密后端。
这里我们使用的是推荐的后端:pyca/cryptography。
哈希密码¶
「哈希」的意思是:将某些内容(在本例中为密码)转换为看起来像乱码的字节序列(只是一个字符串)。
每次你传入完全相同的内容(完全相同的密码)时,你都会得到完全相同的乱码。
但是你不能从乱码转换回密码。
为什么使用哈希密码¶
如果你的数据库被盗,小偷将无法获得用户的明文密码,只能拿到哈希值。
因此,小偷将无法尝试在另一个系统中使用这些相同的密码(由于许多用户在任何地方都使用相同的密码,因此这很危险)。
安装 passlib¶
PassLib 是一个用于处理哈希密码的很棒的 Python 包。
它支持许多安全哈希算法以及配合算法使用的实用程序。
推荐的算法是 「Bcrypt」。
因此,安装附带 Bcrypt 的 PassLib:
$ pip install passlib[bcrypt]
---> 100%
Tip
使用 passlib,你甚至可以将其配置为能够读取 Django,Flask 的安全扩展或许多其他工具创建的密码。
因此,你将能够,举个例子,将数据库中来自 Django 应用的数据共享给一个 FastAPI 应用。或者使用同一数据库但逐渐将应用从 Django 迁移到 FastAPI。
而你的用户将能够同时从 Django 应用或 FastAPI 应用登录。
哈希并校验密码¶
从 passlib 导入我们需要的工具。
创建一个 PassLib 「上下文」。这将用于哈希和校验密码。
Tip
PassLib 上下文还具有使用不同哈希算法的功能,包括仅允许用于校验的已弃用的旧算法等。
例如,你可以使用它来读取和校验由另一个系统(例如Django)生成的密码,但是使用其他算法例如 Bcrypt 生成新的密码哈希值。
并同时兼容所有的这些功能。
创建一个工具函数以哈希来自用户的密码。
然后创建另一个工具函数,用于校验接收的密码是否与存储的哈希值匹配。
再创建另一个工具函数用于认证并返回用户。
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Union
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer, OAuth2PasswordRequestForm
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from pydantic import BaseModel
# to get a string like this run:
# openssl rand -hex 32
SECRET_KEY = "09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7"
ALGORITHM = "HS256"
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
fake_users_db = {
"johndoe": {
"username": "johndoe",
"full_name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"hashed_password": "$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW",
"disabled": False,
}
}
class Token(BaseModel):
access_token: str
token_type: str
class TokenData(BaseModel):
username: Union[str, None] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
email: Union[str, None] = None
full_name: Union[str, None] = None
disabled: Union[bool, None] = None
class UserInDB(User):
hashed_password: str
pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
oauth2_scheme = OAuth2PasswordBearer(tokenUrl="token")
app = FastAPI()
def verify_password(plain_password, hashed_password):
return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
def get_password_hash(password):
return pwd_context.hash(password)
def get_user(db, username: str):
if username in db:
user_dict = db[username]
return UserInDB(**user_dict)
def authenticate_user(fake_db, username: str, password: str):
user = get_user(fake_db, username)
if not user:
return False
if not verify_password(password, user.hashed_password):
return False
return user
def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Union[timedelta, None] = None):
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, SECRET_KEY, algorithm=ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
async def get_current_user(token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme)):
credentials_exception = HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise credentials_exception
token_data = TokenData(username=username)
except JWTError:
raise credentials_exception
user = get_user(fake_users_db, username=token_data.username)
if user is None:
raise credentials_exception
return user
async def get_current_active_user(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
if current_user.disabled:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Inactive user")
return current_user
@app.post("/token", response_model=Token)
async def login_for_access_token(form_data: OAuth2PasswordRequestForm = Depends()):
user = authenticate_user(fake_users_db, form_data.username, form_data.password)
if not user:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Incorrect username or password",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
access_token_expires = timedelta(minutes=ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
access_token = create_access_token(
data={"sub": user.username}, expires_delta=access_token_expires
)
return {"access_token": access_token, "token_type": "bearer"}
@app.get("/users/me/", response_model=User)
async def read_users_me(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return current_user
@app.get("/users/me/items/")
async def read_own_items(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return [{"item_id": "Foo", "owner": current_user.username}]
Note
如果你查看新的(伪)数据库 fake_users_db,你将看到哈希后的密码现在的样子:"$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW"。
处理 JWT 令牌¶
导入已安装的模块。
创建一个随机密钥,该密钥将用于对 JWT 令牌进行签名。
要生成一个安全的随机密钥,可使用以下命令:
$ openssl rand -hex 32
09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7
然后将输出复制到变量 「SECRET_KEY」 中(不要使用示例中的这个)。
创建用于设定 JWT 令牌签名算法的变量 「ALGORITHM」,并将其设置为 "HS256"。
创建一个设置令牌过期时间的变量。
定义一个将在令牌端点中用于响应的 Pydantic 模型。
创建一个生成新的访问令牌的工具函数。
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Union
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer, OAuth2PasswordRequestForm
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from pydantic import BaseModel
# to get a string like this run:
# openssl rand -hex 32
SECRET_KEY = "09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7"
ALGORITHM = "HS256"
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
fake_users_db = {
"johndoe": {
"username": "johndoe",
"full_name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"hashed_password": "$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW",
"disabled": False,
}
}
class Token(BaseModel):
access_token: str
token_type: str
class TokenData(BaseModel):
username: Union[str, None] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
email: Union[str, None] = None
full_name: Union[str, None] = None
disabled: Union[bool, None] = None
class UserInDB(User):
hashed_password: str
pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
oauth2_scheme = OAuth2PasswordBearer(tokenUrl="token")
app = FastAPI()
def verify_password(plain_password, hashed_password):
return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
def get_password_hash(password):
return pwd_context.hash(password)
def get_user(db, username: str):
if username in db:
user_dict = db[username]
return UserInDB(**user_dict)
def authenticate_user(fake_db, username: str, password: str):
user = get_user(fake_db, username)
if not user:
return False
if not verify_password(password, user.hashed_password):
return False
return user
def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Union[timedelta, None] = None):
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, SECRET_KEY, algorithm=ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
async def get_current_user(token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme)):
credentials_exception = HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise credentials_exception
token_data = TokenData(username=username)
except JWTError:
raise credentials_exception
user = get_user(fake_users_db, username=token_data.username)
if user is None:
raise credentials_exception
return user
async def get_current_active_user(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
if current_user.disabled:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Inactive user")
return current_user
@app.post("/token", response_model=Token)
async def login_for_access_token(form_data: OAuth2PasswordRequestForm = Depends()):
user = authenticate_user(fake_users_db, form_data.username, form_data.password)
if not user:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Incorrect username or password",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
access_token_expires = timedelta(minutes=ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
access_token = create_access_token(
data={"sub": user.username}, expires_delta=access_token_expires
)
return {"access_token": access_token, "token_type": "bearer"}
@app.get("/users/me/", response_model=User)
async def read_users_me(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return current_user
@app.get("/users/me/items/")
async def read_own_items(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return [{"item_id": "Foo", "owner": current_user.username}]
更新依赖项¶
更新 get_current_user 以接收与之前相同的令牌,但这次使用的是 JWT 令牌。
解码接收到的令牌,对其进行校验,然后返回当前用户。
如果令牌无效,立即返回一个 HTTP 错误。
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Union
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer, OAuth2PasswordRequestForm
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from pydantic import BaseModel
# to get a string like this run:
# openssl rand -hex 32
SECRET_KEY = "09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7"
ALGORITHM = "HS256"
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
fake_users_db = {
"johndoe": {
"username": "johndoe",
"full_name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"hashed_password": "$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW",
"disabled": False,
}
}
class Token(BaseModel):
access_token: str
token_type: str
class TokenData(BaseModel):
username: Union[str, None] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
email: Union[str, None] = None
full_name: Union[str, None] = None
disabled: Union[bool, None] = None
class UserInDB(User):
hashed_password: str
pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
oauth2_scheme = OAuth2PasswordBearer(tokenUrl="token")
app = FastAPI()
def verify_password(plain_password, hashed_password):
return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
def get_password_hash(password):
return pwd_context.hash(password)
def get_user(db, username: str):
if username in db:
user_dict = db[username]
return UserInDB(**user_dict)
def authenticate_user(fake_db, username: str, password: str):
user = get_user(fake_db, username)
if not user:
return False
if not verify_password(password, user.hashed_password):
return False
return user
def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Union[timedelta, None] = None):
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, SECRET_KEY, algorithm=ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
async def get_current_user(token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme)):
credentials_exception = HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise credentials_exception
token_data = TokenData(username=username)
except JWTError:
raise credentials_exception
user = get_user(fake_users_db, username=token_data.username)
if user is None:
raise credentials_exception
return user
async def get_current_active_user(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
if current_user.disabled:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Inactive user")
return current_user
@app.post("/token", response_model=Token)
async def login_for_access_token(form_data: OAuth2PasswordRequestForm = Depends()):
user = authenticate_user(fake_users_db, form_data.username, form_data.password)
if not user:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Incorrect username or password",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
access_token_expires = timedelta(minutes=ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
access_token = create_access_token(
data={"sub": user.username}, expires_delta=access_token_expires
)
return {"access_token": access_token, "token_type": "bearer"}
@app.get("/users/me/", response_model=User)
async def read_users_me(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return current_user
@app.get("/users/me/items/")
async def read_own_items(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return [{"item_id": "Foo", "owner": current_user.username}]
更新 /token 路径操作¶
使用令牌的过期时间创建一个 timedelta 对象。
创建一个真实的 JWT 访问令牌并返回它。
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Union
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer, OAuth2PasswordRequestForm
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from pydantic import BaseModel
# to get a string like this run:
# openssl rand -hex 32
SECRET_KEY = "09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7"
ALGORITHM = "HS256"
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
fake_users_db = {
"johndoe": {
"username": "johndoe",
"full_name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"hashed_password": "$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW",
"disabled": False,
}
}
class Token(BaseModel):
access_token: str
token_type: str
class TokenData(BaseModel):
username: Union[str, None] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
email: Union[str, None] = None
full_name: Union[str, None] = None
disabled: Union[bool, None] = None
class UserInDB(User):
hashed_password: str
pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
oauth2_scheme = OAuth2PasswordBearer(tokenUrl="token")
app = FastAPI()
def verify_password(plain_password, hashed_password):
return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
def get_password_hash(password):
return pwd_context.hash(password)
def get_user(db, username: str):
if username in db:
user_dict = db[username]
return UserInDB(**user_dict)
def authenticate_user(fake_db, username: str, password: str):
user = get_user(fake_db, username)
if not user:
return False
if not verify_password(password, user.hashed_password):
return False
return user
def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Union[timedelta, None] = None):
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, SECRET_KEY, algorithm=ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
async def get_current_user(token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme)):
credentials_exception = HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise credentials_exception
token_data = TokenData(username=username)
except JWTError:
raise credentials_exception
user = get_user(fake_users_db, username=token_data.username)
if user is None:
raise credentials_exception
return user
async def get_current_active_user(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
if current_user.disabled:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Inactive user")
return current_user
@app.post("/token", response_model=Token)
async def login_for_access_token(form_data: OAuth2PasswordRequestForm = Depends()):
user = authenticate_user(fake_users_db, form_data.username, form_data.password)
if not user:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Incorrect username or password",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
access_token_expires = timedelta(minutes=ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
access_token = create_access_token(
data={"sub": user.username}, expires_delta=access_token_expires
)
return {"access_token": access_token, "token_type": "bearer"}
@app.get("/users/me/", response_model=User)
async def read_users_me(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return current_user
@app.get("/users/me/items/")
async def read_own_items(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
return [{"item_id": "Foo", "owner": current_user.username}]
关于 JWT 「主题」 sub 的技术细节¶
JWT 的规范中提到有一个 sub 键,值为该令牌的主题。
使用它并不是必须的,但这是你放置用户标识的地方,所以我们在示例中使用了它。
除了识别用户并允许他们直接在你的 API 上执行操作之外,JWT 还可以用于其他事情。
例如,你可以识别一个 「汽车」 或 「博客文章」。
然后你可以添加关于该实体的权限,比如「驾驶」(汽车)或「编辑」(博客)。
然后,你可以将 JWT 令牌交给用户(或机器人),他们可以使用它来执行这些操作(驾驶汽车,或编辑博客文章),甚至不需要有一个账户,只需使用你的 API 为其生成的 JWT 令牌。
使用这样的思路,JWT 可以用于更复杂的场景。
在这些情况下,几个实体可能有相同的 ID,比如说 foo(一个用户 foo,一辆车 foo,一篇博客文章 foo)。
因此,为了避免 ID 冲突,当为用户创建 JWT 令牌时,你可以在 sub 键的值前加上前缀,例如 username:。所以,在这个例子中,sub 的值可以是:username:johndoe。
要记住的重点是,sub 键在整个应用程序中应该有一个唯一的标识符,而且应该是一个字符串。
检查效果¶
运行服务器并访问文档: http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs。
你会看到如下用户界面:
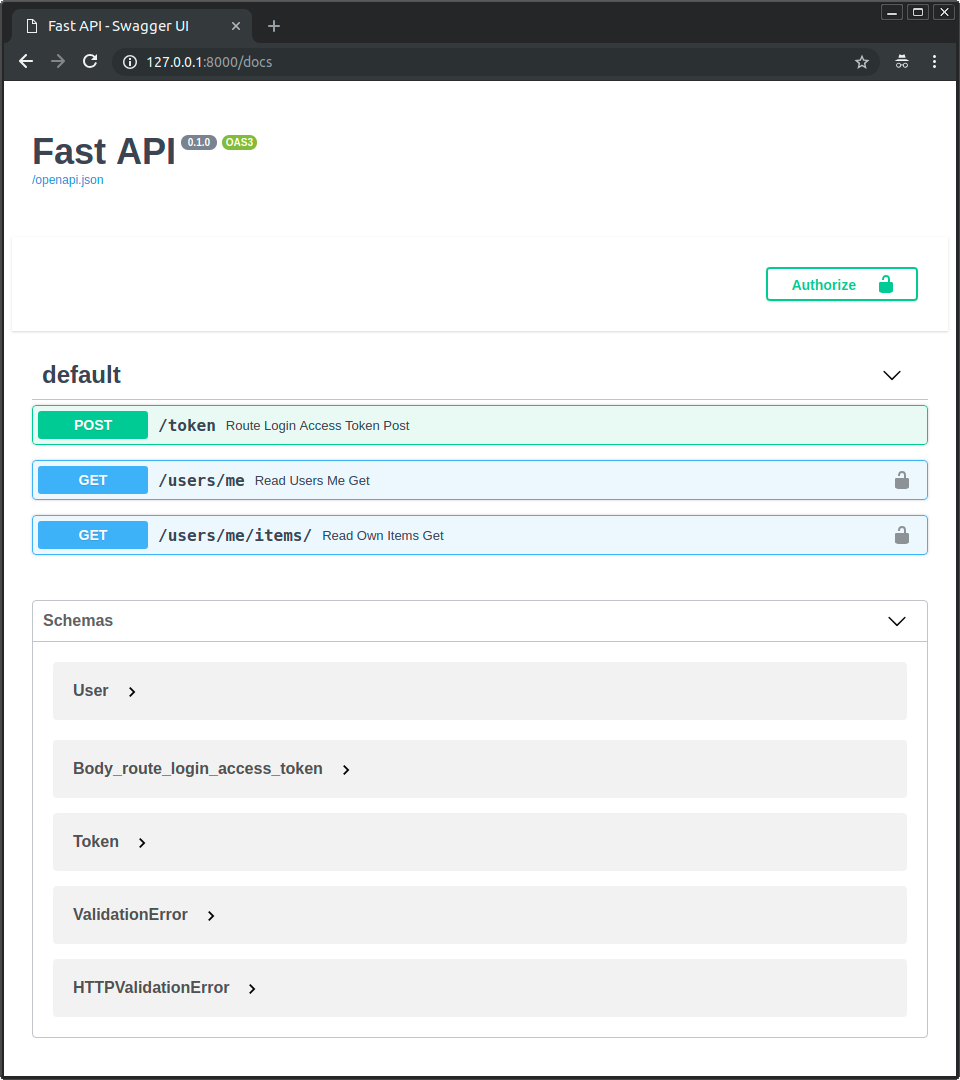
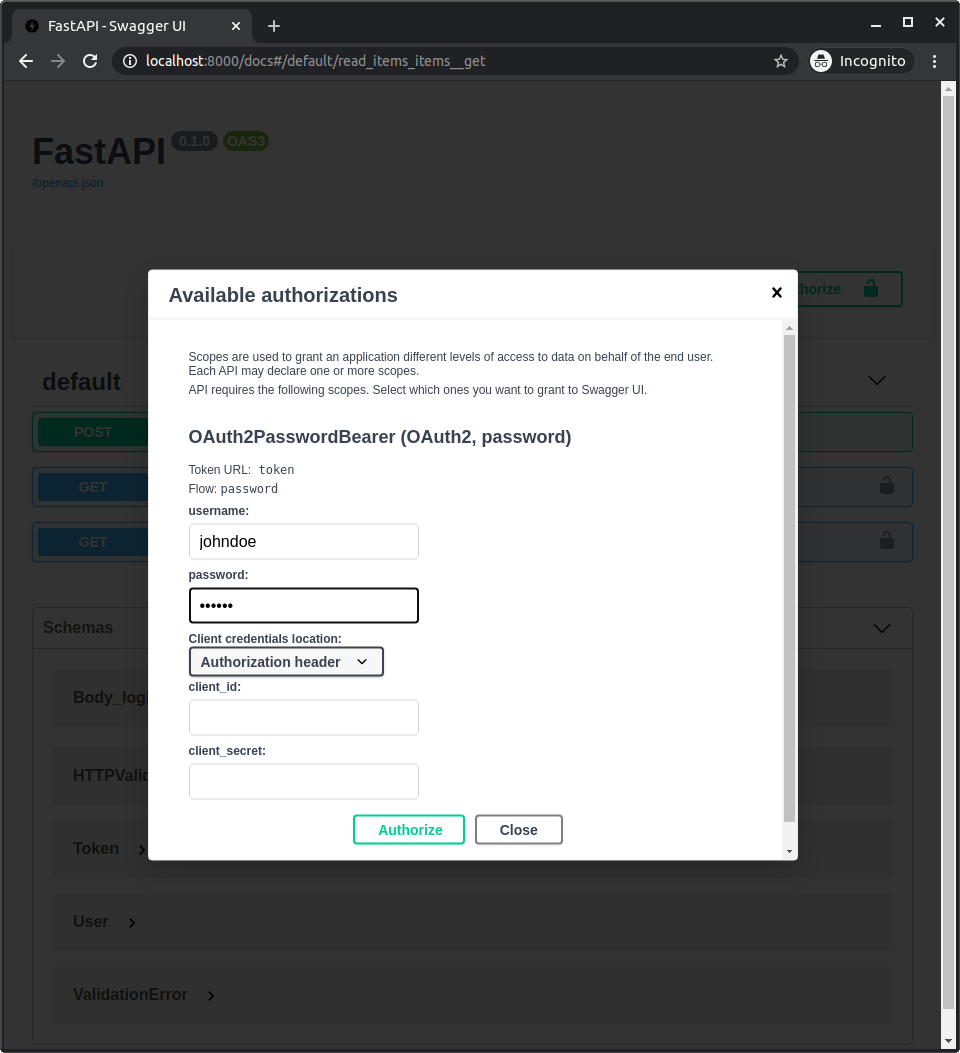
像以前一样对应用程序进行认证。
使用如下凭证:
用户名: johndoe
密码: secret
Check
请注意,代码中没有任何地方记录了明文密码 「secret」,我们只保存了其哈希值。
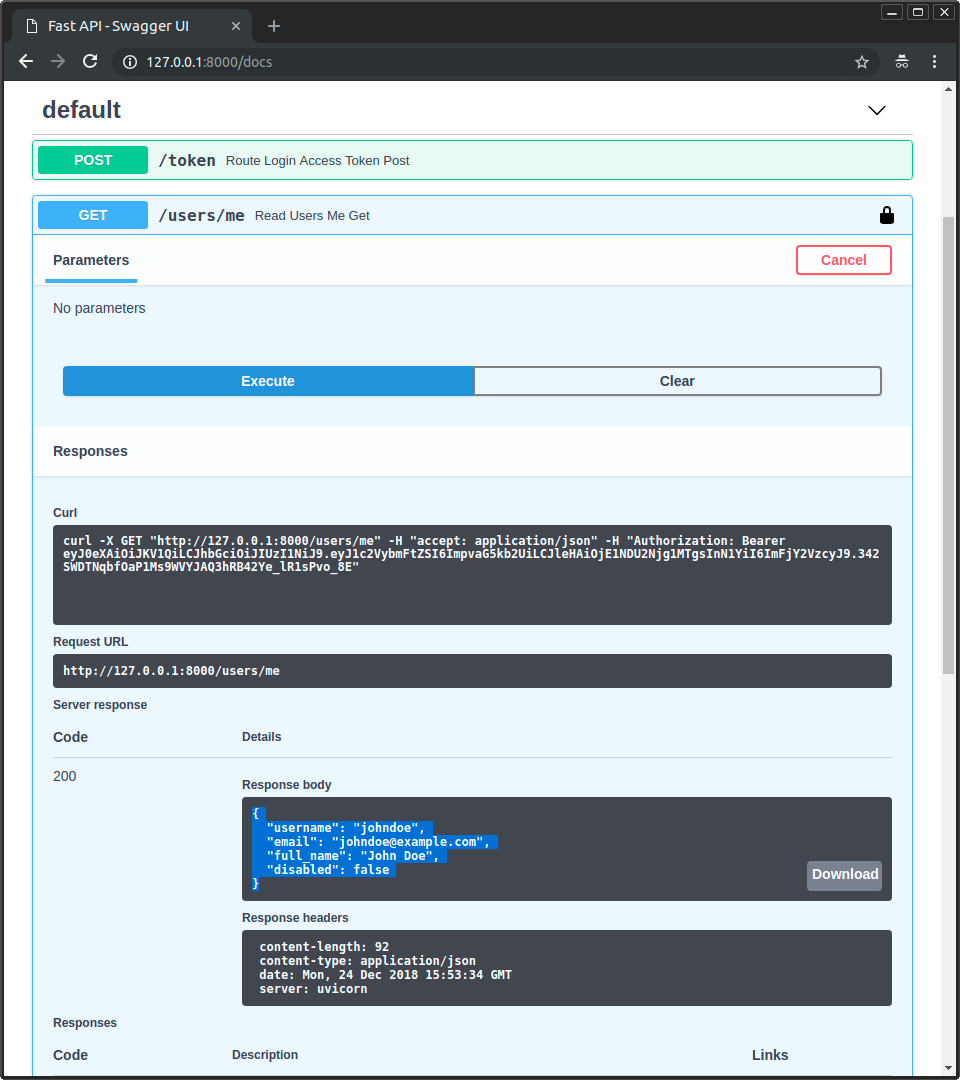
访问 /users/me/ 端点,你将获得如下响应:
{
"username": "johndoe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"full_name": "John Doe",
"disabled": false
}
如果你打开开发者工具,将看到数据是如何发送的并且其中仅包含了令牌,只有在第一个请求中发送了密码以校验用户身份并获取该访问令牌,但之后都不会再发送密码:
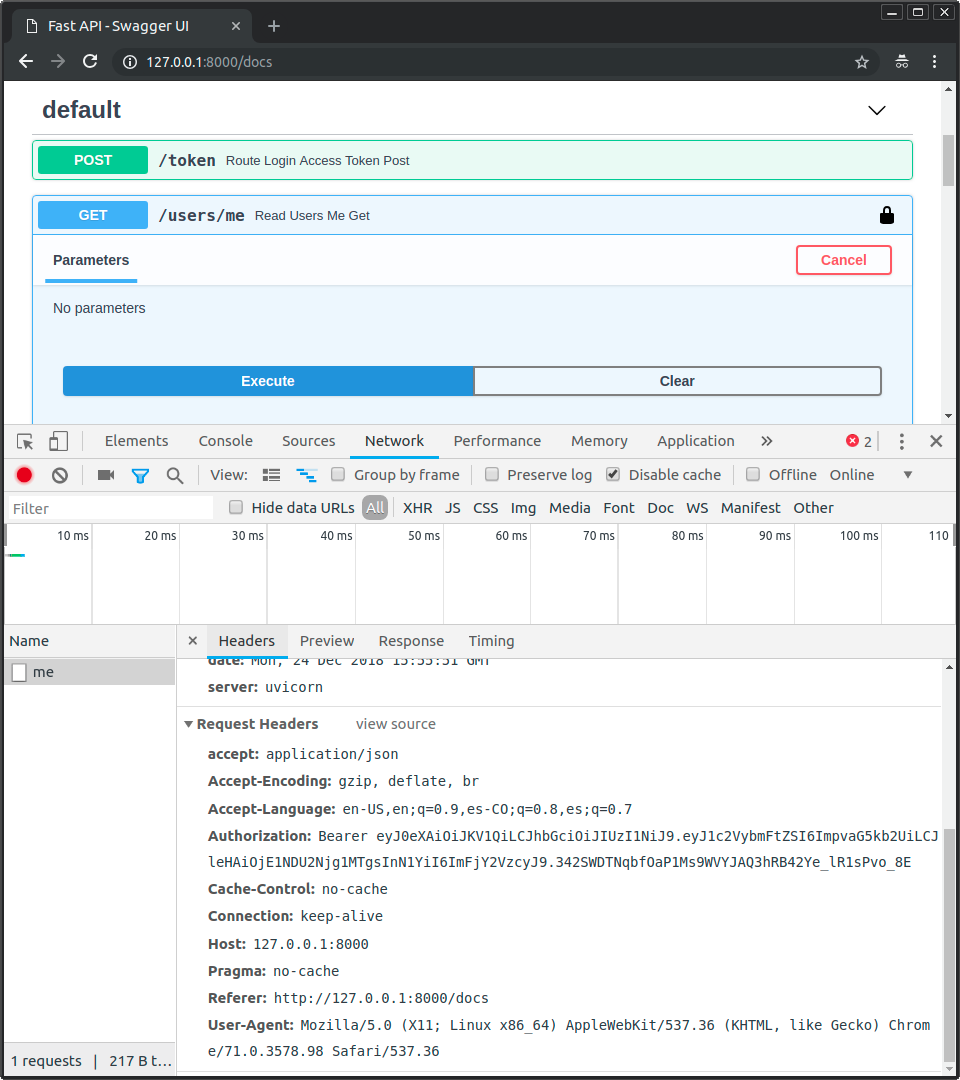
Note
注意请求中的 Authorization 首部,其值以 Bearer 开头。
使用 scopes 的进阶用法¶
OAuth2 具有「作用域」的概念。
你可以使用它们向 JWT 令牌添加一组特定的权限。
然后,你可以将此令牌直接提供给用户或第三方,使其在一些限制下与你的 API 进行交互。
你可以在之后的进阶用户指南中了解如何使用它们以及如何将它们集成到 FastAPI 中。
总结¶
通过目前你所看到的,你可以使用像 OAuth2 和 JWT 这样的标准来构建一个安全的 FastAPI 应用程序。
在几乎所有的框架中,处理安全性问题都很容易成为一个相当复杂的话题。
许多高度简化了安全流程的软件包不得不在数据模型、数据库和可用功能上做出很多妥协。而这些过于简化流程的软件包中,有些其实隐含了安全漏洞。
FastAPI 不对任何数据库、数据模型或工具做任何妥协。
它给了你所有的灵活性来选择最适合你项目的前者。
你可以直接使用许多维护良好且使用广泛的包,如 passlib 和 python-jose,因为 FastAPI 不需要任何复杂的机制来集成外部包。
但它为你提供了一些工具,在不影响灵活性、健壮性和安全性的前提下,尽可能地简化这个过程。
而且你可以用相对简单的方式使用和实现安全、标准的协议,比如 OAuth2。
你可以在进阶用户指南中了解更多关于如何使用 OAuth2 「作用域」的信息,以实现更精细的权限系统,并同样遵循这些标准。带有作用域的 OAuth2 是很多大的认证提供商使用的机制,比如 Facebook、Google、GitHub、微软、Twitter 等,授权第三方应用代表用户与他们的 API 进行交互。